Familiarize yourself with the most common terminologies used in HVUT 2290 tax information reporting, such as EIN, VIN, Taxable Gross Weight (TGW), and 2290 Amendments.
The trucking community is one of the most hardworking communities out there.
That’s a fact.
Every year, around May-June, trucking companies, self-employed truckers, and large fleet owners prepare and file 2290 forms.
This is because the pre-filing season (a specific period allotted to truck tax filers to file their 2290 forms early) begins in May and ends by the end of June of the calendar year.
The actual filing season starts on July 1 of the calendar year.
If you’re wondering, yes; the IRS follows the July-June cycle for truck tax filings.
Now, Form 2290 reporting requires businesses to gather a variety of information as follows:
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
- Business details (EIN, Legal Name, and Address)
- The month of first Use
- Tax suspension details
And more.
If you’re a beginner (Hi! Check out EZ2290), you must be a little confused with all these sound-alike terminologies thrown around.
But don’t worry, this guide will help you get familiar with all such terminologies and give you the context needed to understand them.
So, let’s get to it.
Before we get to the actual terminologies, let’s understand what Form 2290 is for, and its functions.
Understanding Form 2290: Quick Facts
- Form 2290 is an IRS return that specifically deals with heavy highway vehicle usage tax or HVUT.
- Vehicles that weigh 55,000 pounds or more qualify for HVUT taxes. (More on this later)
- HVUT Form 2290 reports certain vehicle information, such as the vehicle weight, month of first use, VIN, and more.
- Form 2290 also reports some basic business details, such as EIN, business address, legal name of the entity, and so on.
- This information helps the IRS identify the business, and use the HVUT reports to tax the entities appropriately.
Now, it’s time to get to the terminologies (the whole reason you’ve clicked on this reading).
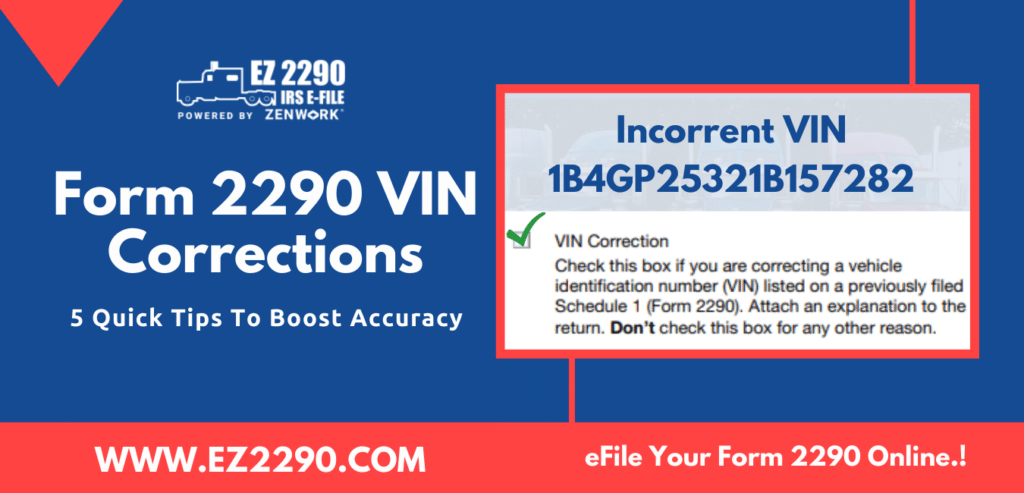
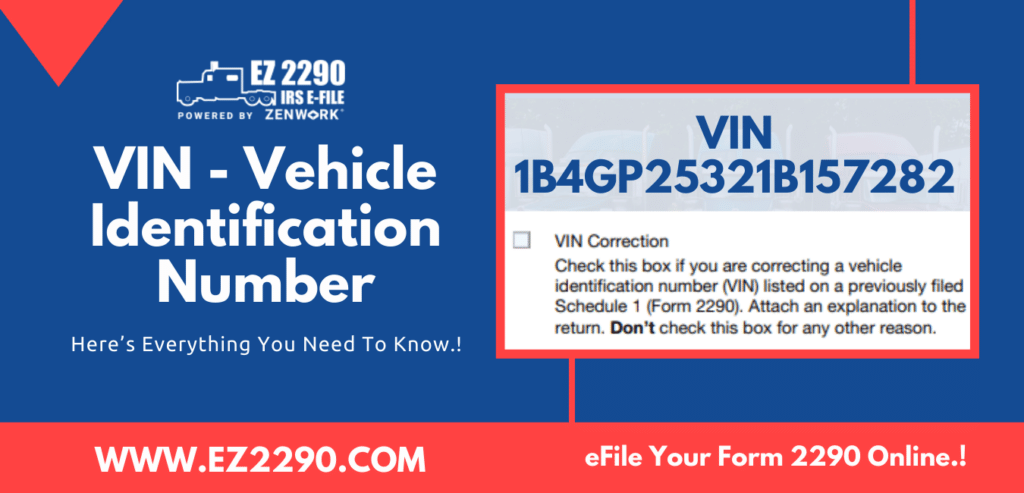
What is a VIN?
V = Vehicle
I = Identification
N = Number
- VIN or Vehicle Identification Number is a unique combination of letters and numbers.
- A VIN is assigned to a vehicle for the purpose of identification.
- It can be used to identify and track the vehicle’s history, right from the date of its manufacturing to its recent traffic records.
- It is a unique code assigned to decode the manufacturer details, geographical origin, registered state, and other critical information about the vehicle.
- HVUT Form 2290 reports the VIN of the vehicle to help the IRS identify the vehicle and its usage status – based on which the IRS taxes the entity.
What is EIN?
E = Employer
I = Identification
N = Number
- Employer Identification Number or EIN is a tax-paying entity’s identification number assigned by the IRS or the social security administration (SSA).
- EIN is a unique code used for identifying a business entity
- In order to get your returns accepted by the IRS, reporting a valid and correct EIN or TIN (taxpayer identification number) is critical.
- Incorrect EIN reports could result in IRS TIN Discrepancy penalties.
What’s the difference between EIN and VIN?
| Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) | Employer Identification Number (EIN) |
| VIN assigned to a vehicle. | EIN is assigned to an employer or a business. |
| VIN is necessary for reporting vehicle-related information. | EIN is mandatory for all information reporting. |
| VIN is used for identifying a vehicle and collecting vehicle information and history. | EIN is used for identifying a business and collecting its compliance history. |
What Is the Taxable Gross Weight of a vehicle?
The total weight of a vehicle, without any prior deductions, is the gross weight of a vehicle.
In the HVUT context, highway vehicles that weigh 55,000 pounds or more, are taxed per their weight and mileage utility.
Here’s a table of the taxable gross weights and the qualified tax range that the IRS uses to tax your trucking company.
What is a 2290 Amendment?
When you file Form 2290, you report all the aforementioned vehicle and business information. However, businesses tend to report information that doesn’t stand valid after filing.
For example, the gross weight of the vehicle could increase after the initial filing has been submitted. Or the mileage use limit of the vehicle could also change.
Factors like this impact the tax burden on your business. And it’s why the IRS recommends businesses to update their reports by “amending” them.
Essentially, when you file a Form 2290 Amendment, you’re “amending” the information and updating the records, so you don’t overpay your HVUT taxes.
Form 2290 Amendment is not a new form, but it must be filed separately.
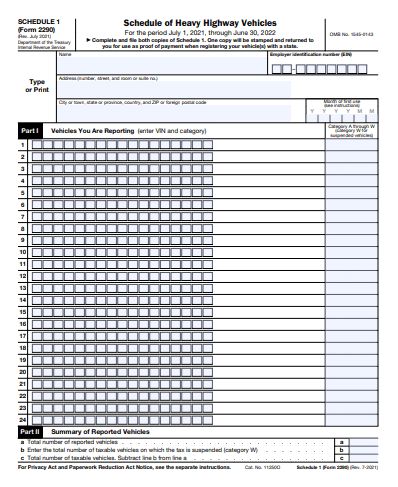
Look at the 2290 form capture below.
If you plan on amending your 2290 reports, then you must file a Form 2290 Amendment.
But to do that, you need to select the “Amended Return” box above.
As you can see, the IRS mandates that 2290 Amendments must be exclusively used for:
- Amending the taxable gross weight of the vehicle
- When the suspended vehicle exceeds its mileage use limit
Note: Suspended vehicles are usually exempt from HVUT as long as they operate within the prescribed miles. However, 2290 filing for tax suspended vehicles is still mandatory.
Where should you eFile Form 2290?
As HVUT compliance experts, we recommend using a simplified eFiling platform like EZ2290, which enables you to eFile Form 2290 online in just 5 super-quick steps.
Step 1: Create your free EZ2290 account
Step 2: Prepare your 2290 forms online
Step 3: Validate your 2290 reports
Step 4: Submit Form 2290 to the IRS
Step 5: Get IRS-stamped Schedule 1 instantly!
No more worrying about paperwork. No hidden costs. No mess.