
Reported An Incorrect VIN On Form 2290? Fix It Quickly & Easily With This Simple Hack!
Follow this simple hack to fix an incorrect VIN report on HVUT Form 2290 easily. Mistakes. All of us are…

Follow this simple hack to fix an incorrect VIN report on HVUT Form 2290 easily. Mistakes. All of us are…
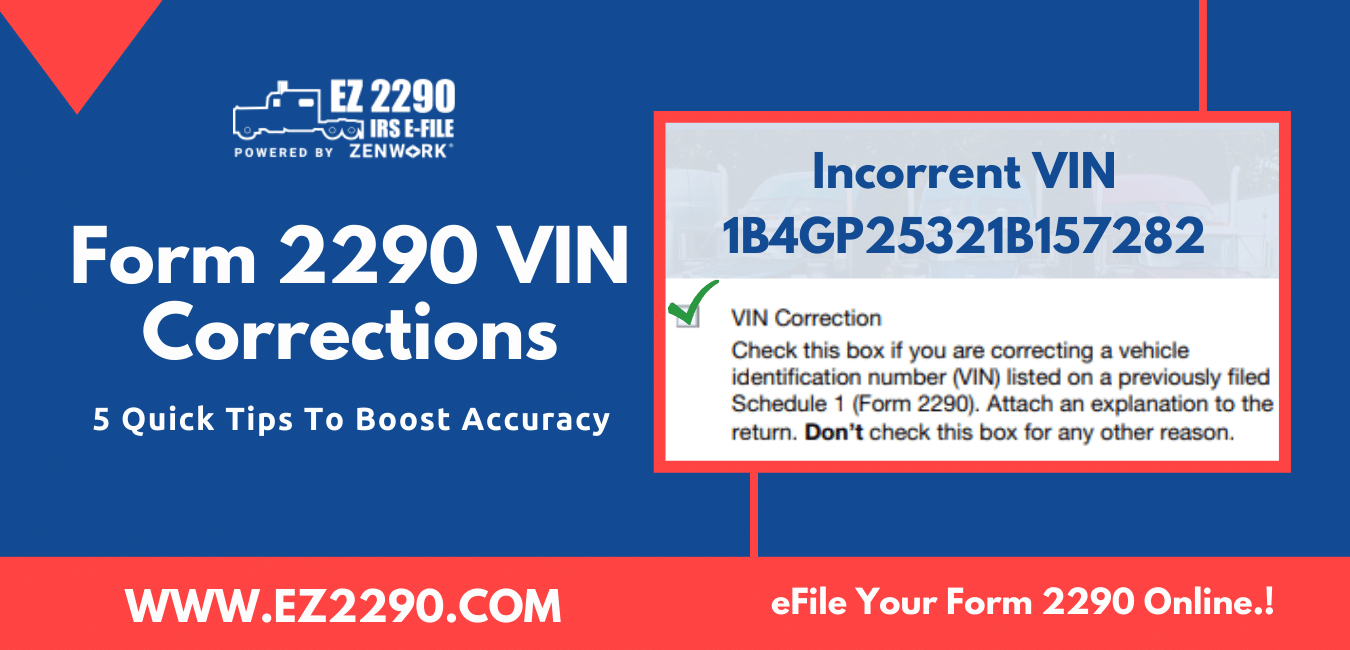
Understand the significance of a vehicle identification number in HVUT e-Files and learn how to eFile Form 2290 VIN Correction…
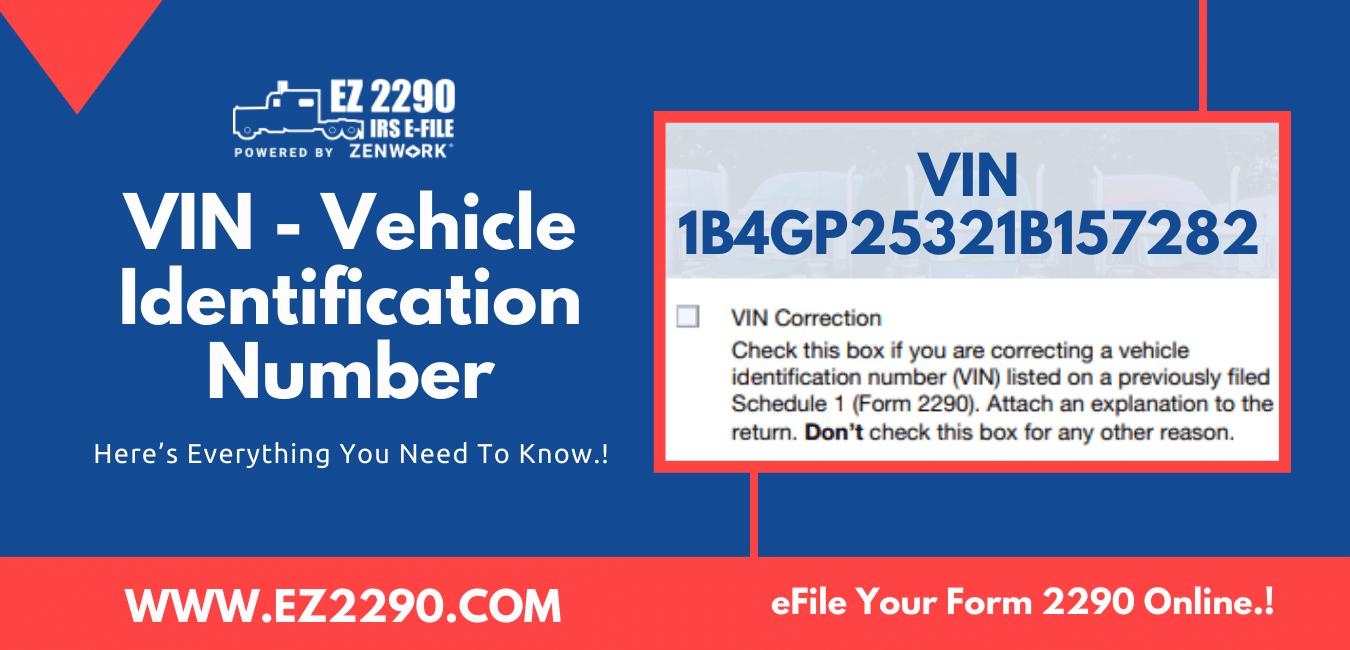
Explore the purpose and uses of Vehicle Identification Number + tips to correct a previously reported incorrect VIN. A vehicle…