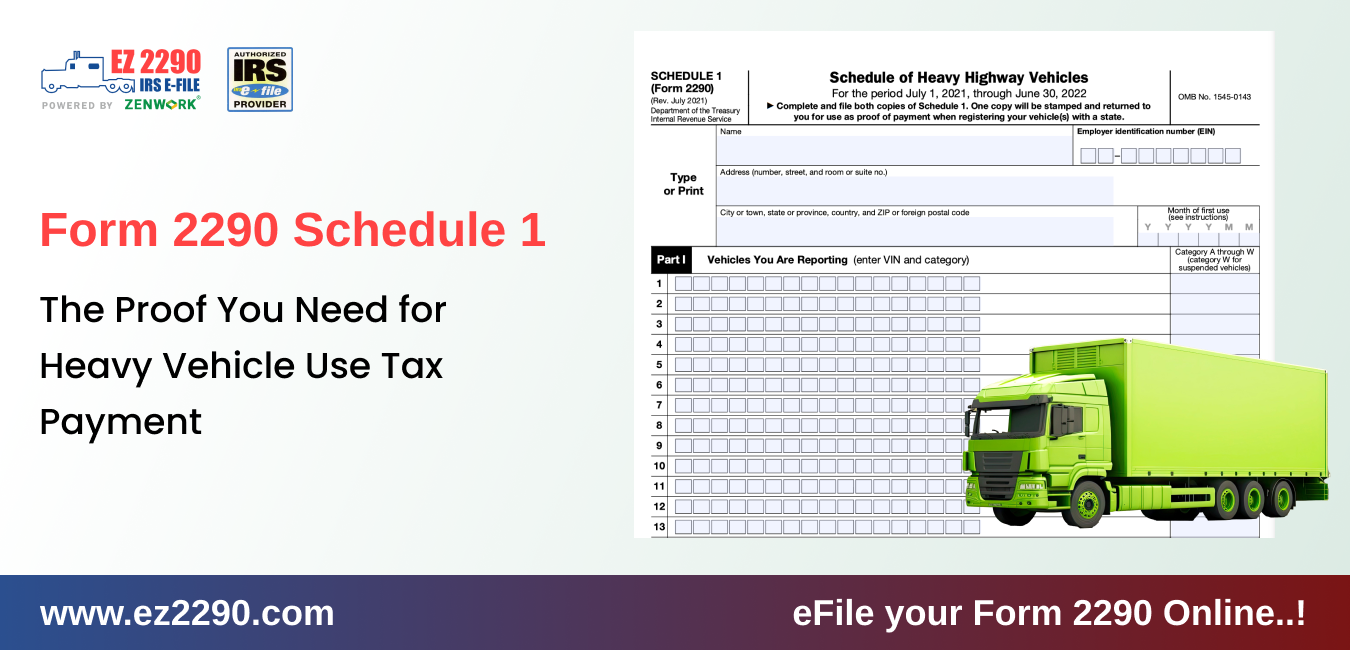
What Is Form 2290 Schedule 1?
Are you a truck driver or fleet owner? If so, you must file Form 2290 and obtain a Schedule 1…

Are you a truck driver or fleet owner? If so, you must file Form 2290 and obtain a Schedule 1…

As a responsible heavy highway vehicle owner, keeping track of IRS deadlines is essential to avoid any potential penalties. Get…

Looking to understand Form 2290 instructions? Look no further than this comprehensive guide, covering everything you need about this critical…

Attention all truck drivers and fleet owners! If you’re unfamiliar with Form 2290, it’s time to rev up your tax…
The last date for filing 2290 form for 2022-23 is here. Hurry up before the deadline ends. If you’ve been…
Just one day left to eFile your 2290 returns before the IRS deadline. Are you ready? Check out this guide…

Learn how EZ2290, an IRS-authorized eFile provider, trusted by 10,000+ trucking companies, drives quick and easy 2290 filings for a…

Here’s how you can report the corrected weight of a heavy vehicle on HVUT Form 2290. Vehicle weight is something…

Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you learn everything about Unified Carrier Registration (UCR). What Is UCR? UCR means Unified…

What to do when your vehicle has less than the HVUT-qualifying mileage limit? And what do you do when you…